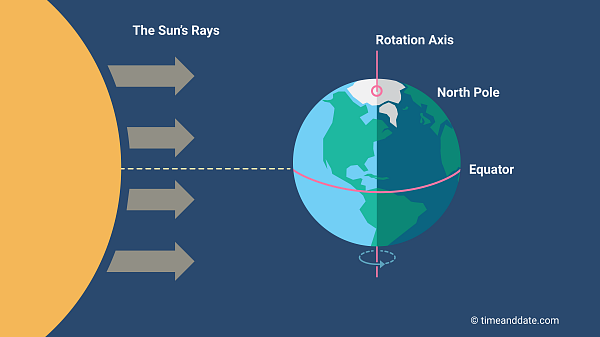
On the equinox, the Earth's axis is perpendicular to the Sun's rays.
March Equinox 2025: Earth’s New Year
Published: Mar 11, 2025
Equal day and night? It can also happen in June!Sun Crosses Celestial EquatorThe March equinox is the moment the
Sun crosses the celestial equator—an imaginary line in the sky above Earth’s equator—
from south to north. This happens on
March 19, 20, or 21 every year.
10 facts about the March equinoxEquinox Local Time & Date
In Lancaster, Pennsylvania, USA:
Thursday, March 20, 2025 at 5:01 am EDT (Change location)This corresponds to Thursday, March 20, 2025 at 09:01 UTC.
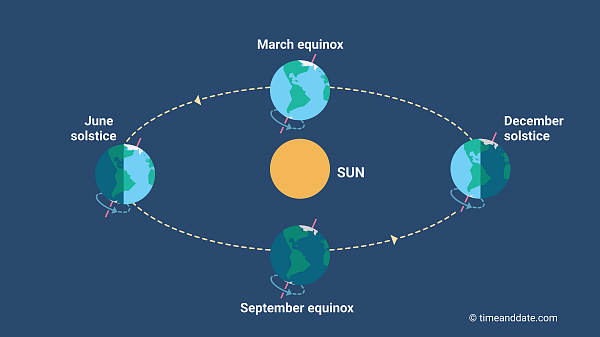
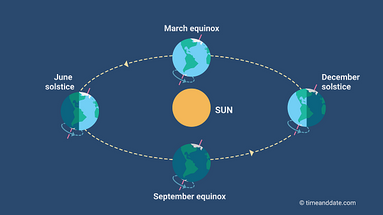
Why Does the Sun Move North and South?During the course of a year, the subsolar point—the spot on the Earth's surface directly beneath the Sun—slowly
moves along a north-south axis. Having reached its southernmost point at the
December solstice, it starts moving northward until it crosses the
equator on the day of the March equinox. The
June solstice marks the northernmost point of its journey.
Earth: The living planetThe Sun: Our home starThe subsolar point moves north and south during the year because the
Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of
about 23.4° in relation to the
ecliptic, an imaginary plane created by Earth’s path around the Sun. In
June, the
Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, and the
subsolar point is north of the equator. As the Earth travels toward the opposite side of its orbit, which it reaches in
December, the Southern Hemisphere gradually receives more sunlight, and the
subsolar point travels south.
How do seasons work?
Earth is tilted as it orbits the Sun, which is why equinoxes and solstices happen.©timeanddate.comWhy Is It Called “Equinox?”On the days of the
equinoxes, the Earth’s axis is
perpendicular to the Sun’s rays, meaning that all regions on Earth receive about the same number of hours of sunlight. In other words,
night and day are, in principle, the
same length all over the world. This is the reason it’s called an “equinox,” derived from Latin, meaning “equal night.”However, this is literal translation
not entirely true. In reality,
equinox days don’t have exactly 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of dark.
Equilux: when day and night are (actually) equalAstronomical terms & definitionsThe Equinoxes and the SeasonsThe March and September equinoxes mark the beginning of the
spring and autumn seasons on Earth,
according to one definition. The equinox in March is the
start of spring in the
Northern Hemisphere and the
beginning of fall south of the equator.
Equinox and solstice dates—years 1-2149Measuring the Tropical YearThe March equinox can be used to measure a
tropical year, the mean time it takes for the Earth to complete a full
orbit around the Sun. Also known as a solar year, a
tropical year is approximately 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, and 45 seconds long. It can vary by up to 30 minutes each year.
Tropical years from 1900 to 2100Why Does the Date Vary?The date of the equinoxes and solstices varies because a year in
our calendar does not exactly match the length of the
tropical year—the time it takes the Earth to complete an orbit around the Sun.Today's
Gregorian calendar has
365 days in a
common year and
366 days in a
leap year. However, our planet takes about
365.242199 days to orbit the Sun. This means that the timing of the equinoxes and solstices slowly
drifts apart from the Gregorian calendar, and the solstice happens about
6 hours later each year. Eventually, the accumulated lag becomes so large that it falls on the following date.To realign the calendar with the tropical year, a
leap day is introduced (nearly) every four years. When this happens, the equinox and solstice dates
shift back to the earlier date again.Other factors influencing the timing of the equinoxes and solstices include variations in the length of a tropical year and in the orbital and daily rotational motion of the Earth, such as the “wobble” in the Earth's axis (precession).
Topics: Astronomy,
Sun,
Seasons,
Equinox,
Earth,
March